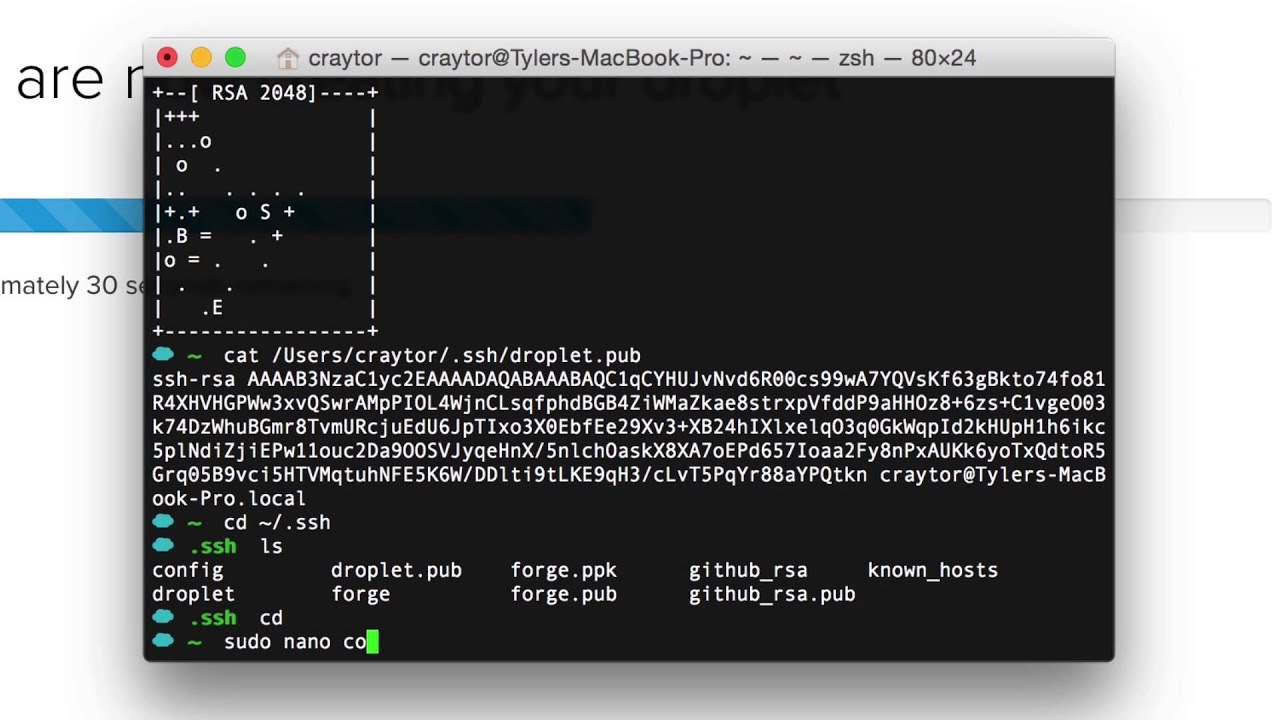
Jan 31, 2010 Create a.ssh directory if it does not already exist and copy the private key in here. You may need to check that the key has the right permissions, type chmod -R g0-rx /.ssh. Enter your ssh command, ssh username@serverhostname.com and hit enter, you should get now have a SSH tunnel to your server. Oct 23, 2017 This guide will show you how to enable SSH (remote login) on your Mac OS X machine and connect to it using a private key file (.ppk) while disabling password logins (more secure). In this example, we will setup the remote connection using Putty. Enable SSH on your Mac. Go to System Preferences - Sharing - Remote Login. Sep 26, 2019 You generate an SSH key through macOS by using the Terminal application. Once you upload a valid public SSH key, the Triton Compute Service uses SmartLogin to copy the public key to any new SmartMachine you provision.
Overview
To use SSH keys on IU Sitehosting, follow the instructions for your OS.
authorized_keys file in the .ssh directory in your account. Any manual changes made to this file will be purged.Generate SSH keys on Linux/Mac
- Generate a public/private key pair:
- Log in to the computer you will use to access Sitehost, and then use the command line to generate a key pair. To generate RSA keys, on the command line, enter:
- You will be prompted to supply a filename (for saving the key pair) and a passphrase (for protecting your private key):
- Filename: To accept the default filename and location for your key pair, press
EnterorReturnwithout entering a filename. Alternatively, you can enter a filename (for example,my_ssh_key) at the prompt, and then pressEnterorReturn. - Passphrase: Enter a passphrase that contains at least five characters, and then press
EnterorReturn. If you pressEnterorReturnwithout entering a passphrase, your private key will be generated without password protection.
- Filename: To accept the default filename and location for your key pair, press
- Once the key pair has been generated, navigate to the location where you saved the public key.
- Copy the contents of your public key (this is the file with the
.pubextension). - Once you copy the contents of your public key, see Add a public key to IU Sitehosting below.
Generate SSH keys on Windows
- Install PuTTY. The PuTTY command-line SSH client, the PuTTYgen key generation utility, the Pageant SSH authentication agent, and the PuTTY SCP and SFTP utilities are packaged together in a Windows installer available under The MIT License for free download from the PuTTY development team.
- Launch PuTTYgen.
- In the 'PuTTY Key Generator' window, under 'Parameters':
- For 'Type of key to generate', select RSA. (In older versions of PuTTYgen, select SSH2-RSA.)
- For 'Number of bits in a generated key', leave the default value (
2048).
- Under 'Actions', click Generate.
- When prompted, use your mouse (or trackpad) to move your cursor around the blank area under 'Key'; this generates randomness that PuTTYgen uses to generate your key pair.
- When your key pair is generated, PuTTYgen displays the public key in the area under 'Key'. In the 'Key passphrase' and 'Confirm passphrase' text boxes, enter a passphrase to passphrase-protect your private key.
If you don't passphrase-protect your private key, anyone with access to your computer will be able to SSH (without being prompted for a passphrase) to your account on any remote system that has the corresponding public key.
- Right-click in the 'Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file' text box, choose Select All, and then right-click in the text box again and select Copy.
- Save your private key in a safe place. You'll use the passphrase any time you log into a Sitehost server using SSH keys, and you'll need to copy the public key to your profile on the WebTech website. To save your private key:
- Under 'Actions', next to 'Save the generated key', click Save private key.
If you didn't passphrase-protect your private key, the utility will ask whether you're sure you want to save it without a passphrase. Click Yes to proceed or No to go back and create a passphrase for your private key.
- Keep 'Save as type' set to PuTTY Private Key Files (*.ppk), give the file a name (for example,
putty_private_key), select a location on your computer to store it, and then click Save. - If you wish to connect to a remote desktop system such as Research Desktop (RED), click Conversions > Export OpenSSH key, give the file a name (for example,
putty_rsa), select a location on your computer to store it, and then click Save.
- Under 'Actions', next to 'Save the generated key', click Save private key.
If you no longer have the public key, or if it is later determined to be invalid, use the following steps to obtain a public key:
- Launch PuTTYgen.
- Click Load.
- Navigate to your private key and click Open.
- In the PuTTYgen pop-up window, enter the passphrase.
- Right-click in the 'Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file' text box, choose Select All, and then right-click in the text box again and select Copy.
- Select File > Exit to close PuTTYgen.
Add a public key to IU Sitehosting
- Go to the IU Sitehosting account management.
- At the top right, click Sign in, and, if prompted, log in with your IU username and passphrase.
- At the top right, click your name. You'll be taken to the 'Manage your profile' page.
- Under 'Manage SSH keys':
- In the 'Note' field, enter a short description.
- In the 'Public Key' field, paste the public key you copied in step 7 above.
- Click Add. If the public key is valid, it will be added to your profile. Within 30 minutes, the public key will be added to all sitehost-test and sitehost accounts that you own, or for which you are a proxy or developer.
Connect to IU Sitehosting using SSH keys in various applications
You generate an SSH key through macOS by using the Terminal application. Once you upload a valid public SSH key, the Triton Compute Service uses SmartLogin to copy the public key to any new SmartMachine you provision.
Joyent recommends RSA keys because the node-manta CLI programs work with RSA keys both locally and with the ssh agent. DSA keys will work only if the private key is on the same system as the CLI, and not password-protected.
About Terminal
Terminal is the terminal emulator which provides a text-based command line interface to the Unix shell of macOS.
To open the macOS Terminal, follow these steps:
- In Finder, choose Utilities from the Applications folder.
- Find Terminal in the Utilities listw.
- Open Terminal.
The Terminal window opens with the commandline prompt displaying the name of your machine and your username.
Generating an SSH key
An SSH key consists of a pair of files. One is the private key, which should never be shared with anyone. The other is the public key. The other file is a public key which allows you to log into the containers and VMs you provision. When you generate the keys, you will use ssh-keygen to store the keys in a safe location so you can bypass the login prompt when connecting to your instances.
To generate SSH keys in macOS, follow these steps:
-
Enter the following command in the Terminal window.
This starts the key generation process. When you execute this command, the
ssh-keygenutility prompts you to indicate where to store the key. -
Press the ENTER key to accept the default location. The
ssh-keygenutility prompts you for a passphrase. - Type in a passphrase. You can also hit the ENTER key to accept the default (no passphrase). However, this is not recommended.
You will need to enter the passphrase a second time to continue.
Generate Ssh Private Key Mac Torrent
After you confirm the passphrase, the system generates the key pair.
Your private key is saved to the id_rsa file in the .ssh directory and is used to verify the public key you use belongs to the same Triton Compute Service account.
| Never share your private key with anyone! |
|---|
Your public key is saved to the id_rsa.pub;file and is the key you upload to your Triton Compute Service account. You can save this key to the clipboard by running this:
Importing your SSH key

Now you must import the copied SSH key to the portal.
- After you copy the SSH key to the clipboard, return to your account page.
- Choose to Import Public Key and paste your SSH key into the Public Key field.
- In the Key Name field, provide a name for the key. Note: although providing a key name is optional, it is a best practice for ease of managing multiple SSH keys.
- Add the key. It will now appear in your table of keys under SSH.
Troubleshooting
You may see a password prompt like this:
This is because:
- You did not enter the correct passphrase.
- The private key on your Macintosh (
id_rsa) does not match the public key stored with your Triton Compute Service account. - The public key was not entered correctly in your Triton account.
What are my next steps?
Mac Generate Ssh Private Key
Right in the portal, you can easily create Docker containers, infrastructure containers, and hardware virtual machines.
Generate Ssh Key Windows
In order to use the Terminal to create instances, set up triton and CloudAPI as well as the triton-docker commandline tool.